Know how this clever CristalACTiV coating can clean the air !!
How CristalACTiV Works
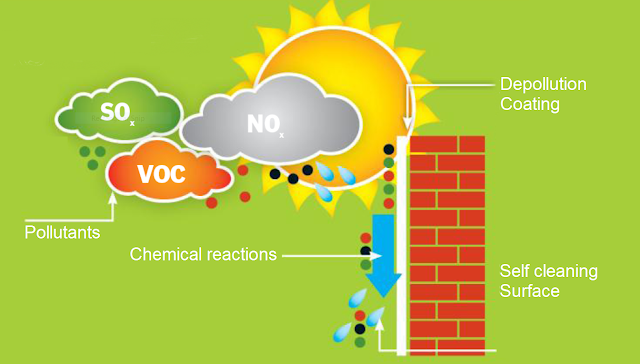
This clever coating can be painted on structures to help cleanse the surrounding air
1) Pollutants
Photoreactive atmospheric pollutants like VOCs, NOx, and Sox come into contact with the depollution coating.
2) Depollution coating
Under the sun’s UV light, the titanium dioxide (TiO2) coating forms highly reactive free radical particles, capable of breaking down pollutants.
3) Chemical reactions
Photocatalytic reactions involving the free radicals convert pollutants to carbon dioxide, water, and harmless compounds that stick to the depollution surface.
4) Self-cleaning surface
The soiled surface is washed clean whenever rain falls, or it is hosed down.
Photocatalysis
In some cases, airborne pollutants convert to harmless materials when they react chemically with other atmospheric gases. These reactions happen naturally in the presence of light but on a slow timescale. In photocatalysis, the rate of these common reactions is boosted using a specific catalyst. Innovative chemical company Cristal has pioneered a pollution-busting coating that can be painted directly onto buildings. Made from ultra-fine photocatalytic titanium dioxide (TiO2), it actively draws pollutants including VOCs, NOx and sulphur dioxides from the surrounding air and converts them into harmless by-products that are easily blown away. Best of all, the catalyst itself is not used up in the reaction, so its performance never dips.
Air Pollution
With the potential to cross international boundaries, air pollution is a truly global problem
Air pollution is the influx of gases and particles into the atmosphere that has adverse effects on living creatures and the organized environment. According to the World Health Organisation (WHO), 7 million premature deaths are caused every year by people breathing polluted air – that’s one in eight deaths globally. Once released into the environment, pollutants are impossible to hold and depending on prevailing weather patterns it has the potential to affect people who are hundreds or even thousands of kilometers away from the source.
Over the last half-century, the nature of this problem has changed. In the developed world, smog-causing discharges of poisonous smoke, sulphur dioxide and particulates associated with incomplete fuel combustion have been checked by technologies like flue-gas desulphurization systems, soot scrubbers, and catalytic converters. Gases that deplete the stratospheric ozone layer most aggressively have been banned and replaced by harmless compounds, and today it’s the threat of global warming that appears to be the largest.
There is a growing indication, however, that respiratory problems like asthma might really be caused by air pollution, not just triggered by it. Some researchers have even made tentative links between neighborhood air quality and rates of childhood autism.
As with other forms of pollution, the best way to protect the environment is to avoid releasing these toxic elements in the first place. Conserving electricity, driving mindfully, and choosing to walk, cycle or take public transport are easy alternatives we can all make in order to breathe just a little easier.
Atmospheric Pollutants
The major contributors to
environmental damage
This gas is produced when fossil fuels burn incompletely, with road vehicles being the predominant source.
2) Ozone (O3)
This is formed when other pollutants react in the presence of heat and sunlight. It triggers lung irritation and asthma attacks.
3) Nitrogen oxides (NOx)
These form during fossil fuel combustion and contribute to global warming, smog including ground-level ozone formation.
4) Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
In the presence of pollutants, these carbon-based chemicals contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone and smog
.
5) Sulphur dioxide (SO2)
This is produced during incomplete combustion in coal-fired power stations and fireplaces. It contributes to smog and acid rain.
6) Particulates
These include airborne dust, dirt, soot, and smoke. They can cause respiratory problems and environmental damage, such as acidification of lakes.
If you want this webpage in doc format
Download link of this 👉 Article(Google Docs)
If you want this webpage in doc format
Download link of this 👉 Article(Google Docs)








Comments
Post a Comment